Prerequisites
This article assumes that you’ve set up hadoop 2.4.0 and also cloned Spark git repository.
Building Spark for Hadoop 2.4.0 and YARN
To enable YARN support and build against the correct hadoop libraries (for v2.4.0), set the SPARK_YARN and SPARK_HADOOP_VERSION variables while building the spark assembly
$ cd /usr/local/spark
$ SPARK_HADOOP_VERSION=2.4.0 SPARK_YARN=true sbt/sbt clean assembly
Specifying the clean task is important as sbt sometimes mixes up jars from the default hadoop 1.0.4 version and the specified hadoop 2.4.0 version. Doing an explicit clean prevents this problem.
After this step, an assembly JAR for Spark with Hadoop 2.4.0 and YARN support will be created at the following location
./assembly/target/scala-2.10/spark-assembly-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-hadoop2.4.0.jar
Running an example Spark program on YARN
$ cd /usr/local/spark
$ SPARK_JAR=./assembly/target/scala-2.10/spark-assembly-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-hadoop2.4.0.jar HADOOP_CONF_DIR=/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop ./bin/spark-submit --master yarn --deploy-mode cluster --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi --num-executors 3 --driver-memory 4g --executor-memory 2g --executor-cores 1 examples/target/scala-2.10/spark-examples-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-hadoop2.4.0.jar
This runs the application in yarn cluster mode. It starts a new yarn client program and the SparkPi code is then run as a child thread of the ApplicationMaster. Since the application is run on a remote machine, interactive applications can’t work this way (e.g. spark-shell). Refer to the next section for details on running such applications.
You can view cluster details on the YARN web interface (http://localhost:8088)
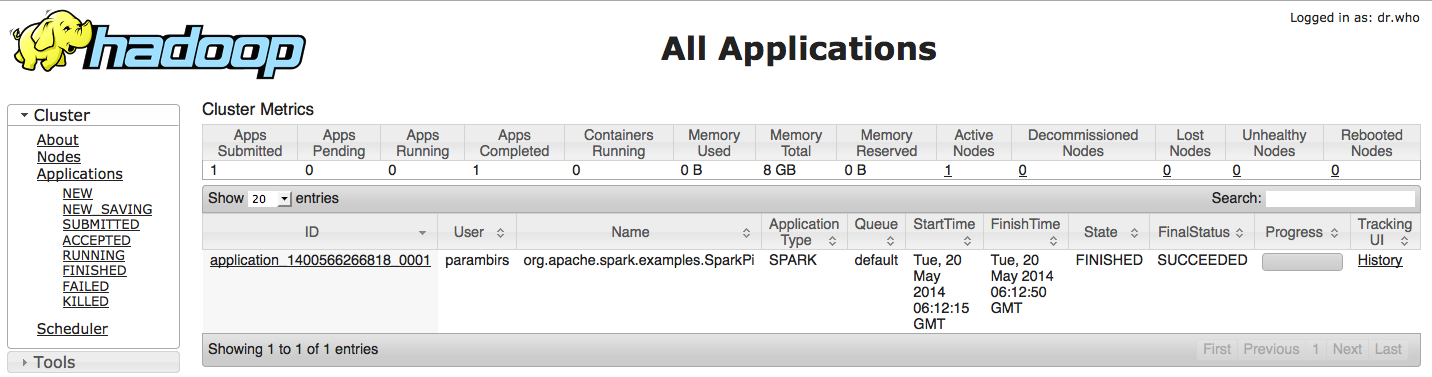
The output of YARN apps isn’t printed on the console. To see the output of this app, we’ll have to go through the app’s logs. YARN logs generally go into the $HADOOP_HOME/logs/userlogs/application_ folder. You can get the appID from the YARN web interface or YARN output printed on the console.
$ cat /usr/local/hadoop/logs/userlogs/application_1400566266818_0001/container_1400566266818_0001_01_000001/stdout
...
Pi is roughly 3.1429
You can also see the logs from the web interface by navigating to YARN_App > history > logs
Running Spark Shell on YARN
With yarn-client mode, the application is launched locally (like in local mode). To run spark-shell in yarn-client mode, use the following command
$ SPARK_JAR=./assembly/target/scala-2.10/spark-assembly-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-hadoop2.4.0.jar HADOOP_CONF_DIR=/usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop MASTER=yarn-client ./bin/spark-shell
You can see that this launches an application on YARN using the web interface
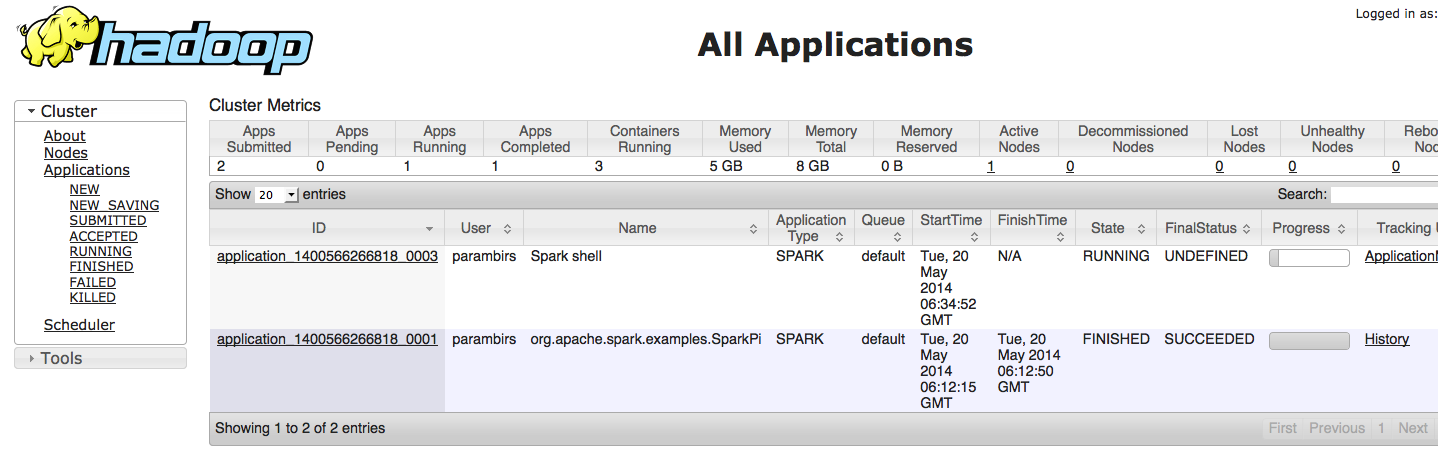
Let’s try out some commands in the spark-shell
scala> val textFile=sc.textFile("file:///usr/local/spark/README.md")
textFile: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[String] = MappedRDD[1] at textFile at <console>:12
scala> textFile.count
res0: Long = 126
scala> textFile.filter(_.contains("the")).count
res1: Long = 28
scala> exit
When running in yarn-client mode, it’s important to start local file URIs with file://. This is because in this mode, spark assumes that files are present in HDFS (in the /user/<username>) directory. For example, try the following commands in the spark-shell
scala> val textFile=sc.textFile("README.md")
textFile: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[String] = MappedRDD[1] at textFile at <console>:12
scala> textFile.count
org.apache.hadoop.mapred.InvalidInputException: Input path does not exist: hdfs://localhost:9000/user/parambirs/README.md